About Heart Failure
Heart failure is a serious and expensive medical condition in which the heart is unable to meet the demands of its workload. As a result, the body’s organs may not receive enough oxygen, disrupting their normal function. The patient will be out of breath and experience a range of other symptoms.
Fluid Overload in Heart Failure
When the heart cannot keep up, the body retains water and salt. This is commonly referred to as a fluid overload, edema, or congestion. The extra fluid in turn increases the burden on the weakened heart.
There are several forms of heart failure and heart failure may have different causes. Retaining water and salt and symptoms of fluid overload can occur with all forms.
Fluid overload causes episodes of worsening heart failure. Sometimes this can be reversed with a higher dose or oral diuretics. Often it cannot and patients need to be admitted for IV treatment.
When the patient is admitted they often have more than two gallons of extra fluid that needs to come off.
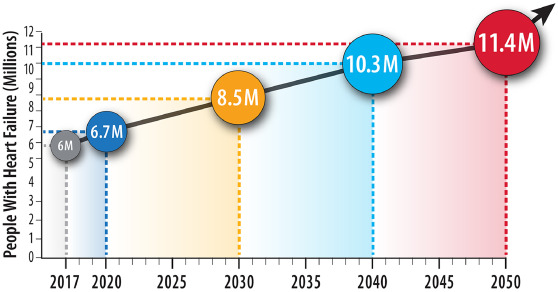
Heart Failure is Very Common
Approximately 1 in 4 persons will develop HF in their lifetime. Approximately 6.7 million Americans over 20 years of age have heart failure (HF). This is expected to rise to 8.7 million in 2030 and over 10 million in 2040.
Prevalence of Heart Failure and Future Projection if Current Trends Continue. Source: HFSA 2024
Source: Fonarow GC et.al. American Heart Journal.
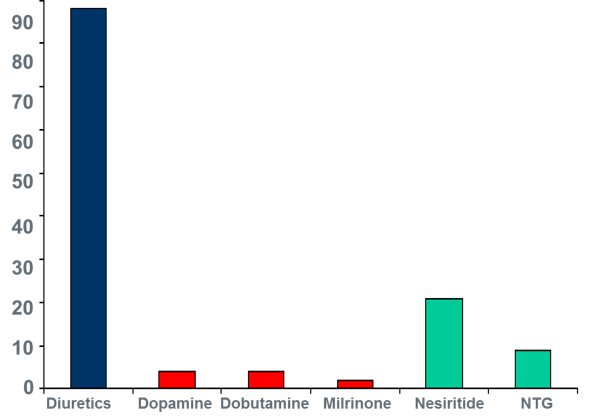
When Hospitalized the Main Treatment is Diuretics
Over 90% of patients with fluid overload are treated with diuretics alone. These medications help the body eliminate excess fluid and salt by increasing urine production in the kidneys. Removing this extra fluid reduces the strain on the weakened heart and improves symptoms.
For more than 50 years, furosemide, the active ingredient in Lasix®, has been the primary diuretic for heart failure patients.
Currently, however, most patients receive furosemide intravenously, leading to long and burdensome hospital stays and high treatment costs.
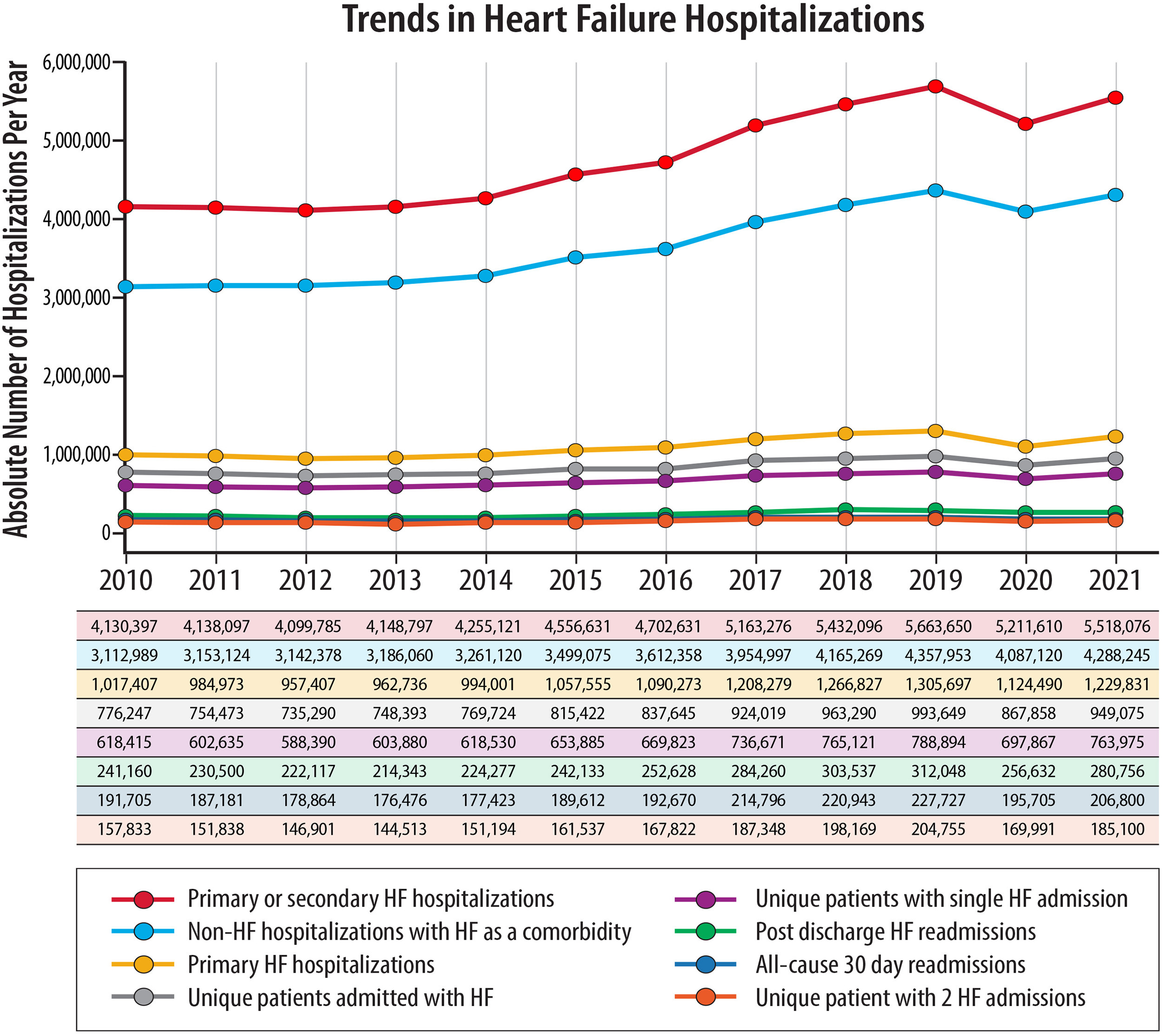
A Leading Cause of Hospitalizations
Emergency room visits and hospitalizations are common for fluid overload in heart failure. It is the second most common reasons for hospital admission in individuals over the age of 65. Hospitalizations for heart failure are a major burden for the hospital systems, the payors and above all for patients and their family. Approximately 1.3M heart failure hospitalizations occur in the US each year and the number is rising.
Hospitalizations are hard on patients, particularly the elderly. They often lose muscle mass, self-care functions, and are at risk for complications from the stay. There is also the burden and stress for the family and loved ones.
Source: HF STATS 2024: Heart Failure Epidemiology and Outcomes Statistics An Updated 2024 Report from the Heart Failure Society of America. Bozkurt, Biykem et al. Journal of Cardiac Failure, Volume 0, Issue 0
The High Cost of Heart Failure
Heart failure is a leading cause of high-cost inpatient care. The most common reason for hospital admissions is fluid overload which is treated with IV diuretics over a several day in-patient stay in the hospital.
The problem is expected to double over the next 10 years because of the aging population and increased survival.
Our goal is to reduce the financial burden of heart failure while improving treatment options. The healthcare cost that subcutaneous furosemide may impact is $14.4 billion. *
* Cost of medicare for treatment of worsening heart failure in the U.S. (2015)

A Better Way
We believe that patients should not have to be admitted into a hospital just to receive effective diuretic treatment.
Our team at SQ Innovation has developed the a subcutaneous Infusor to provide hospital IV-strength diuresis for at-home use.
The new drug and Infusor received tentative Approval in October 2024. This means it meets all FDA requirements but is not yet approved for sale.